A closer look: Burners and boilers
The installation of energy-efficient burner and boiler technology offers energy-saving opportunities in heat supply systems. Burner and boiler applications are used both on a small scale in the private sector and on a very large scale in the industrial sector.
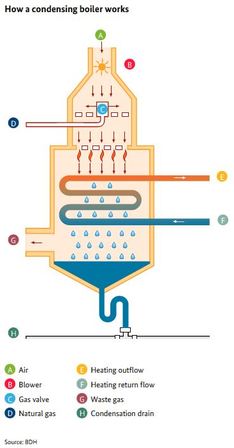
Unlike conventional boilers, condensing gas boilers recover the heat contained in waste gases using additional heat transfer surfaces. The hot water vapour contained in the exhaust gas after combustion of the gas-air mixture is used for this purpose. Cold feedwater is passed over the heat transfer surfaces through the hot water vapour. The feedwater is thus preheated, while the steam is cooled so that it condenses. Condensing boilers have a much lower exhaust gas temperature and energy content than conventional gas boilers, which accounts for their greater efficiency.
Waste heat recovery boilers use heat from waste gases, or exhaust gases as they are also known. The exhaust gases from combustion processes or hot exhaust air flows are used to generate hot water or steam. For this purpose, the hot exhaust gas is passed through a tube bundle which transfers its heat to the water in the boiler.
The following burners and processes are especially relevant for furnaces:
- Flameless oxidation (FLOX) is a highly efficient burner technology that allows compliance with strict nitrogen oxide (NOX) limits, even at high combustion air-preheating temperatures.
-
Due to the high exhaust velocity of the combustion gases, these high-speed or high-momentum burners ensure that the combustion chamber gases are internally recirculated in the combustion chambers, thus achieving uniform distribution of temperature. These burners are therefore more efficient than conventional burners.
- Combustion with pure oxygen in furnaces offers some advantages over combustion with air: The combustion temperature and combustion efficiency are significantly higher using this process: combustion with pure oxygen reduces the waste gas volume flow and also results in a considerable decrease in exhaust gas losses.



